3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that transforms digital files into solid three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer. Where traditional manufacturing usually involves cutting or hollowing material, 3D printing builds objects from the ground up, layer by layer. This innovative process opens up exciting possibilities for industries and individuals alike, allowing for the creation of complex geometries, rapid prototyping, and customized products at lower costs.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
3D printing involves creating an object by collecting layers of material - whether it’s plastic, metal, or resin. A digital 3D model serves as the blueprint, typically designed in computer-aided design (CAD) software. The model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers, which the printer follows to gradually build up the physical object.
The time required to print an object depends on factors like the size, material, type of printer, and level of detail needed. Depending on the project's complexity, print times can range from a few minutes to several days.
Types of 3D Printing
Not all 3D printers work the same way. There are several methods of 3D printing, each suited for different materials and purposes. Here are the seven major types of 3D printing -
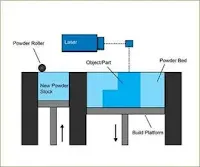
1. Powder Bed Fusion (PBF)
PBF uses thermal energy, typically from lasers, to fuse layers of powder material (e.g., metal or plastic) into solid parts. This method is widely used for manufacturing durable and complex components, especially in the aerospace and automotive industries. Popular forms include Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
2. VAT Photopolymerization
This method uses light to cure liquid resin in a vat, creating solid layers one at a time. There are two main types: Stereolithography (SLA), which uses a UV laser, and Digital Light Processing (DLP), which projects an entire layer image onto the resin. These processes are ideal for intricate prototypes, though the output can be brittle.
3. Binder Jetting
In binder jetting, layers of powder are glued together using a binding agent. This technique is often used for making metal, ceramic, or full-color parts. The process usually requires post-processing, such as sintering, to enhance the strength of the finished product.
4. Material Jetting
Similar to an inkjet printer, this method deposits tiny droplets of material that harden into a solid. Material jetting is precise and can print in multiple colors and materials simultaneously. However, it tends to be more expensive and is primarily used for detailed models rather than functional parts.
5. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
The most common type of 3D printing for hobbyists and general-purpose manufacturing, FDM extrudes heated filament (plastic or other materials) through a nozzle. This affordable, easy-to-use process is widely used for prototypes but lacks the high strength and detail of other methods.
6. Sheet Lamination
In this process, thin sheets of material are layered and fused by adhesive or ultrasonic welding. While it’s not as precise as other methods, it is often used for creating large metal parts at a lower cost.
7. Direct Energy Deposition (DED)
DED uses focused thermal energy (like a laser or electron beam) to melt wire or powder material as it is deposited layer by layer. It’s mainly used for metal parts and allows repairs or modifications to existing components.
Applications of 3D Printing
The flexibility and speed of 3D printing have led to its adoption across many industries. Let’s look at some of the key areas where 3D printing is making a big impact -
1. Construction
3D printing in construction has the potential to reduce labor costs and build time. Large-scale concrete 3D printers can print modular building components or entire structures like walls and foundations. Notable projects include the first 3D-printed bridge in Spain and the world's first fully 3D-printed house in Russia.
2. Prototyping and Manufacturing
One of the original purposes of 3D printing was rapid prototyping, allowing businesses to quickly create prototypes and test designs. In manufacturing, 3D printing is increasingly used to produce custom parts, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) are common methods for creating production parts, not just prototypes.
3. Healthcare
3D printing is transforming healthcare, from creating personalized prosthetics and dental devices to printing implants like hip and knee joints. Researchers are even exploring 3D printing for bioprinting tissue, organs, and surgical tools. Its ability to customize for individual patients makes it a game-changer in the medical field.
4. Aerospace
The aerospace industry uses 3D printing for prototyping, design optimization, and even producing critical components. It enables engineers to create lightweight parts with complex geometries, reducing both production time and fuel costs.
5. Automotive
Automotive companies use 3D printing for rapid prototyping and even for manufacturing certain parts. High-performance racing teams, such as those in Formula 1, rely on 3D printing to create customized components for better performance. In the future, we may see 3D printing used for the on-demand production of spare parts.
Top 3D Printing Software
3D printing relies heavily on software to create models and control the printing process. Here are some of the top software solutions used today:
MatterControl 2.0 - An all-in-one design and printing platform for creating, slicing, and controlling your 3D prints.
Tinkercad- A simple, free, browser-based tool for beginners to design 3D models.
Blender - A powerful open-source software for 3D modeling, rendering, and animation.
Ultimaker Cura - A beginner-friendly slicing software compatible with many 3D printers.
Conclusion -
3D printing has evolved from a niche technology used for prototyping to a mainstream solution with wide-ranging applications in industries like healthcare, construction, aerospace, and manufacturing. Its ability to produce complex, customized, and lightweight components at lower costs is unlocking new possibilities for innovation.
As technology advances, 3D printing is set to revolutionize the way we design, build, and manufacture products across the globe. Whether you’re a hobbyist, an engineer, or a healthcare professional, 3D printing is a tool worth exploring.








Comments
Post a Comment